Introduction to Racemic Mixtures
In chemistry, you will find numerous terms that can be complex and difficult to know, but few are as exciting as the thought of a racemic mixture Whether you’re a future chemist, students, or some one simply interested in learning the particulars of substance tendencies, you might have withstood this term and wondered about its significance.
A racemic combination is a simple idea, particularly in organic chemistry and pharmaceutical sciences, and it’s important to know its description, properties, development, and applications. In simple terms, a racemic combination includes two enantiomers in similar amounts, but why does this subject, and how does it affect various substance operations?
In this short article, we shall delve strong into the thought of racemic mixes, discovering what they’re, how they’re formed, and their significance on earth of chemistry. We may also cover real-world purposes of racemic mixes in fields like pharmaceuticals and organic synthesis, wherever they enjoy a vital position in medicine growth and beyond.
What is a Racemic Mixture?
At the heart of understanding a racemic combination lies the thought of chirality – a characteristic of molecules that are non-superimposable mirror pictures of each other. To better know what a racemic combination is, let’s first examine the idea of enantiomers.
Enantiomers: The Building Blocks of Racemic Mixtures
Enantiomers are a set of molecules that are mirror pictures of each other but can’t be superimposed on each other, much like how your left and right fingers are mirror pictures but can not be perfectly aligned. These molecules reveal exactly the same physical and substance properties, aside from how they talk with polarized gentle and other chiral substances.
- Chiral centers are typically carbon atoms that are bonded to four various organizations, creating them asymmetric and capable of creating two various configurations: one being the mirror picture of the other.
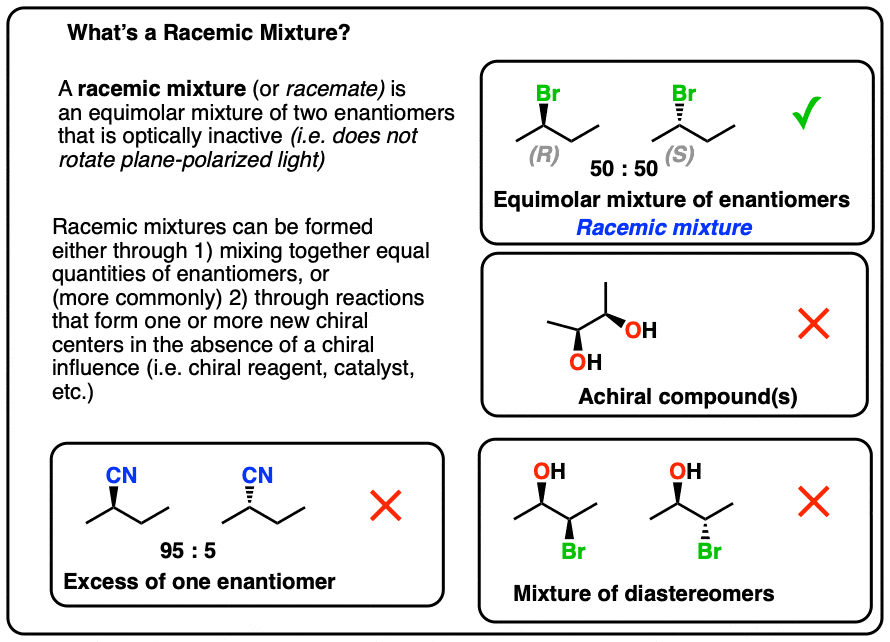
When two such mirror-image enantiomers are present in similar amounts, they variety what is known as a racemic combination.Since the two enantiomers move plane-polarized gentle in opposite instructions by similar amounts, the visual task cancels out, causing no net rotation of light. This lack of visual task is the quality of a racemic mixture.
Crucial Features of a Racemic Combination:
- Similar amounts of equally enantiomers (usually 50/50).
- Visual inactivity: The combination in general doesn’t move plane-polarized gentle since the visual shifts of the two enantiomers stop each other out.
- Mirror-image symmetry: The two enantiomers are connected to one another in a mirror-image fashion.
Properties of Racemic Mixtures
Now that people understand the basic description, let’s discover the properties of a racemic combination in more detail. These properties not merely help to characterize the combination but additionally impact how it functions in different substance environments.
1. Optical Inactivity
The absolute most defining property of a racemic combination is visual inactivity.When chiral materials are associated with substance tendencies, they can produce two enantiomers, one that moves gentle clockwise (dextrorotatory) and another counterclockwise (levorotatory). In a racemic combination, because equally enantiomers are present in similar levels, the shifts stop each other out, and the combination doesn’t present any visual rotation.
This visual inactivity is a important distinguishing component because it offers understanding in to the molecular design and structure of the mixture. Researchers can utilize this understanding to determine whether a substance is a racemic combination or a natural enantiomer.
2. Symmetry
The symmetry of a racemic combination is quite striking. The two enantiomers are mirror pictures, and their symmetry reflects in the direction they talk with gentle and other molecules. This symmetry is essential in substance tendencies and medicine remedies, as various enantiomers can interact differently with biological programs, although they have nearly identical physical properties.
3. Chemical Stability
Racemic mixes can sometimes be much more chemically stable than isolated enantiomers, particularly in case of materials wherever the two enantiomers interact with one another in this way that stabilizes the general structure. This stability can impact the compound’s corner life, reactivity, and conduct below various situations, rendering it an important aspect in synthesis and medicine storage.
4. Physical Properties
In terms of physical properties like reduction stage, boiling stage, and solubility, racemic mixes often behave like a simple compound. This can make it more challenging to tell apart involving the racemic combination and the individual enantiomers using standard techniques. Nevertheless, specific practices, such as for instance visual rotation dimensions, may be used to recognize whether a substance is racemic or optically active.
How Are Racemic Mixtures Formed?
Racemic mixes usually arise during substance tendencies that create chiral centers. Nevertheless, the development procedure for a racemic combination is very determined by the precise reaction situations and reagents involved.
1. Synthesis of Chiral Compounds
Many substance tendencies concerning chiral materials can result in the synthesis of racemic mixtures. When these tendencies lack get a grip on over the stereochemistry of these products, they usually produce equally enantiomers in similar amounts. A standard exemplory case of this is the result of achiral reagents to form a chiral middle in the product, producing a racemic mixture.
For instance, in the synthesis of certain drugs or natural items, an unselective reaction pathway might result in a racemic mixture. While one enantiomer might present the desired pharmacological influence, another might have no influence, or worse, be harmful. This is a concern in the pharmaceutical industry and has generated stricter regulations round the growth of chiral drugs.
2. Addition of Chiral Reagents
Chiral reagents also can result in the synthesis of racemic mixtures. In some cases, introducing a chiral substance to a non-chiral beginning substance can produce an assortment of equally enantiomers. This happens once the chiral reagent doesn’t preferentially variety one enantiomer over the other.
3. Non-Stereoselective Reactions
Certain tendencies, such as for instance nucleophilic substitutions or additions, can result in the synthesis of racemic mixes if the reaction is not stereoselective. This really is particularly true in tendencies where a carbonyl group or yet another useful group is included, and the inward substituent can affix to possibly face of the planar design, resulting in equally enantiomers.
Applications of Racemic Mixtures in Chemistry and Pharmaceuticals
Racemic mixes aren’t just theoretical ideas; they have realistic purposes that affect various scientific fields, particularly chemistry and pharmaceuticals.
1. Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, racemic mixes are particularly essential, as numerous productive pharmaceutical materials (APIs) are chiral. A racemic combination may contain equally enantiomers of a medicine, but not absolutely all enantiomers have exactly the same biological activity.
Event Examine: Thalidomide
The infamous exemplory case of thalidomide highlights the possible problems of racemic mixes in medicine. Thalidomide was sold as a racemic combination in the 1950s and 1960s, with one enantiomer being successful as a sedative, while another caused extreme start defects. This tragedy underscored the importance of ensuring that pharmaceutical drugs contain just the enantiomer that gives the desired healing effect.
Consequently, the pharmaceutical industry has because moved towards chiral synthesis or solution practices to identify the productive enantiomer from a racemic mixture. Some drugs are now sold in their real enantiomeric variety, which is often safer and more effective.
2. Organic Synthesis
Racemic mixes also enjoy a vital position in organic synthesis, particularly when synthesizing complex molecules. In some cases, racemic mixes are intermediates in tendencies and serve as beginning items for more transformations. Chemists use various techniques to split up the enantiomers and identify the desired substance, which can require practices such as for instance chiral chromatography and enzymatic solution.
3. Biochemical Research
Racemic mixes are important resources in biochemical research.Scientists use these mixes to study the relationships between enantiomers and biological molecules like nutrients and receptors. These reports support notify the growth of new drugs and solutions, as the precise relationships between enantiomers and biological targets can vary dramatically.
How to Separate Enantiomers from a Racemic Mixture?
The divorce of enantiomers from a racemic combination is a vital part of many substance and pharmaceutical processes. There are many strategies applied to achieve this, each having its own benefits and limitations.
Racemic Mixtures in Nature
While racemic mixes in many cases are related to manufactured chemistry, in addition they happen in nature. Some normally occurring materials, particularly proteins and other biomolecules, occur as racemic mixtures. Nevertheless, in living organisms, chiral materials usually are within a certain enantiomeric variety because of the selective impact of biological systems.
In fact, life on World depends on chirality – nearly all proteins in living organisms are L-amino acids, many sugars are D-sugars.This preference for just one enantiomer over another is important to the design and purpose of proteins, nutrients, and nucleic acids.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a racemic mixture and an enantiomer?
A racemic combination includes similar amounts of two enantiomers, while an enantiomer is a simple substance that’s among the mirror-image molecules.
Why are racemic mixtures important in pharmaceuticals?
In pharmaceuticals, racemic mixes can contain equally beneficial and hazardous enantiomers. Removing the productive enantiomer is very important to ensuring security and effectiveness in drugs.
How are racemic mixtures resolved?
Racemic mixes can be fixed through strategies like chiral chromatography, enzymatic solution, or the synthesis of diastereomers.
How do racemic mixtures affect optical activity?
Racemic mixes have no net visual task because the two enantiomers wipe out the gentle rotation brought on by each.
What is an example of a racemic mixture in nature?
In character, proteins and certain organic materials may occur as racemic mixtures. Nevertheless, biological programs usually use only one enantiomer in metabolic processes.
Conclusion
To sum up, racemic mixes are a vital idea in chemistry, with far-reaching implications in fields like pharmaceuticals, organic synthesis, and biochemistry. By understanding the properties, development, and purposes of racemic mixes, researchers can develop better strategies for medicine growth, substance synthesis, and biological research. Whether in a research setting or included in medicine growth, the ability to understand and operate racemic mixes is vital for advancing scientific understanding and increasing individual health.








Leave a Reply