Introduction: What is Marginal Benefit?
When it comes to making choices, whether in personal life or organization Marginal Benefit ,understanding the minor benefit is crucial. This idea, seated in economics, assists people and companies evaluate whether yet another action or expense provides worthwhile value. In this article, we’ll dive heavy into what minor benefit is, how it’s calculated, and why it’s essential for making educated decisions.
The Concept of Marginal Benefit Explained
Limited benefit identifies the additional gain or pleasure that a individual gets from consuming or producing an additional device of an excellent or service. It plays a crucial role in reference allocation and decision-making processes.
For example, imagine you’re deciding whether to get an extra piece of pizza. The pleasure (or benefit) you get from that additional piece is the minor benefit. If you’re presently full, the minor benefit decreases. This shows what the law states of decreasing minor returns, which we will examine further in this article.
How to Calculate Marginal Benefit
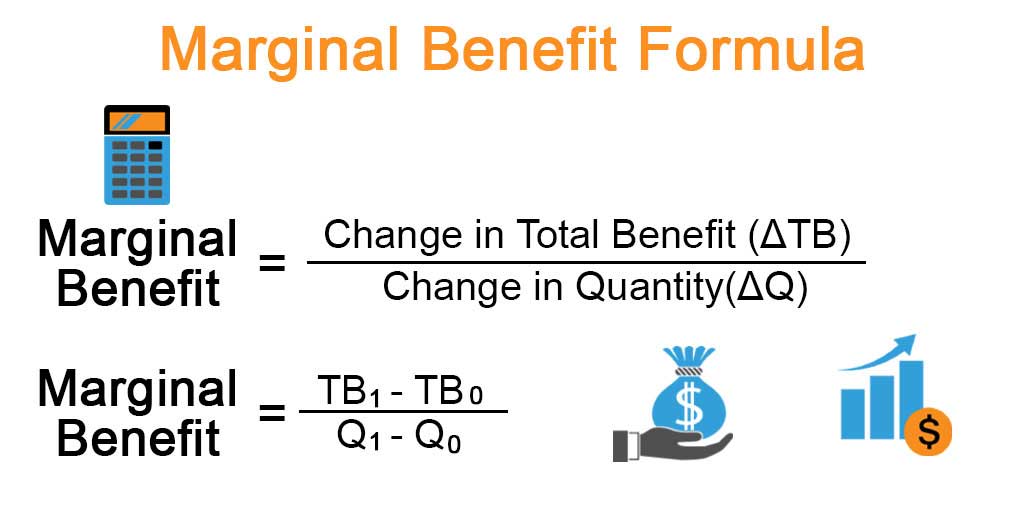
To calculate minor benefit, you simply divide the modify altogether benefit by the modify in quantity of the good or company consumed. The system is:
Marginal Benefit=Change in Total BenefitChange in Quantity\textMarginal Benefit = \frac\textChange in Full Benefit\textChange in QuantityMarginal Benefit=Change in QuantityChange in Total Benefit
This formula is essential for determining if yet another expense or action is worthwhile. In operation, minor benefit assists companies enhance production and marketing strategies by focusing on activities that bring the most additional value.
Marginal Benefit vs. Marginal Cost
While minor benefit is about the additional price received, minor price identifies the additional price of producing an additional device of an excellent or service. Understanding the relationship between these two is type in making wise decisions. If the minor benefit exceeds the minor price, it’s often value continuous the activity. Nevertheless, if the minor price outweighs the power, it might be time for you to reconsider.
Real-World Applications of Marginal Benefit
1. Customer Decision-Making
Everyday, customers automatically calculate minor benefits when deciding whether to get items or services. For example, think about a individual deciding whether to cover premium loading services. If the minor benefit—additional reveals, no ads—exceeds the minor price, they will likely make the purchase.
2. Organization Technique
Firms use minor benefit to judge their investments. Businesses evaluate whether producing an additional device of a product provides additional profit. If the minor benefit is better than the minor price of production, it’s an intelligent organization move to continue.
3. Public Policy
Governments also contemplate minor benefits when designing policies. For example, when deciding whether to purchase public infrastructure, policymakers consider the possible benefits (such as financial development or decreased travel times) from the costs.
The Importance of Marginal Benefit in Economic Theory
Limited benefit is foundational in financial principle, specially in understanding customer behavior. As persons digest more of an excellent, the minor benefit typically decreases—a principle known as decreasing minor utility. This fall explains why customers do not keep getting the exact same object forever, also when they like it.
Marginal Benefit and the Law of Diminishing Returns
The legislation of decreasing minor returns shows that as you keep on to boost consumption of an excellent, the added pleasure (marginal benefit) from each additional device decreases. For this reason, following a specific level, producing or consuming more may possibly not be beneficial.
For example, a factory may experience decreasing returns when it hires too many workers. Originally, each new staff improves production, but following a level, overcrowding may lower effectiveness, reducing the minor benefit of choosing more staff.
Marginal Benefit in Pricing and Marketing
Pricing strategies frequently joint on minor benefit. Businesses evaluate what individuals are ready to cover yet another device and set rates accordingly. When companies realize their customers’ minor benefits, they are able to fine-tune their marketing communications to highlight the added price of these products.
Optimizing Resource Allocation with Marginal Benefit
For people and companies, understanding the minor benefit is critical to optimizing reference allocation. By concentrating initiatives on parts where in fact the minor benefit is high, resources can be used more effectively, major to raised outcomes.
For example, an organization may invest more in marketing routes that bring a higher minor benefit, such as for instance social media campaigns with strong involvement prices, while climbing back on less powerful methods.
How Marginal Benefit Affects Personal Finance Decisions
Understanding minor benefit also can increase personal fund decisions. Whether you’re investing, keeping, or spending, consider the minor benefit of each economic choice. For example, deciding to save lots of an extra $100 might have a higher minor benefit in the long term than spending it on a luxurious object today.
Common Pitfalls When Ignoring Marginal Benefit
Ignoring minor benefit may result in poor decision-making. For example, an organization that over-invests in a product with decreasing returns may waste resources, or even a customer who purchases a lot more than required might experience economic stress without additional satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What’s the minor benefit of consuming more of a product?
The minor benefit is the additional pleasure or price you gain from consuming an additional device of a product. It can help in determining if the additional use may be worth the cost.
2. How is minor benefit distinctive from total benefit?
While total benefit is the general pleasure from consuming a product, minor benefit stresses just on the pleasure received from another device consumed.
3. Can minor benefit actually be negative?
Yes, minor benefit may be negative when consuming more of a product leads to unhappiness or a decline in overall energy, such as for instance overeating or overspending.
4. So how exactly does minor benefit relate to organization choices?
Firms use minor benefit to judge the possible gain from producing or selling an additional device of a product. This can help in optimizing production and pricing strategies.
5. What role does minor benefit enjoy in public policy?
Governments contemplate minor benefit when assessing guidelines to ensure that the advantages to culture justify the costs included, resulting in more effective allocation of public resources.








Leave a Reply